Install Webalizer On Ubuntu Server Desktop
How to install Webmin on Cent. OS 7. Webmin is a web- based graphical tool for unix . It is used to manage services like User management, Disk managemet, Network, Iptables (Firewall), Cron, Apache, DNS, File sharing and much more . In this article i will show you how to install webmin on Cent. OS 7 linux. To get started, login your remote server and follow the steps below: First, create a new filewebmin. Enable webmin Port: firewall- cmd - -add- port=1. Now, open http: //ip.
Installing and configuring IPTables Firewall A guide for the home webmaster. Last updated: 5/10/2008. This document assumes you have. Install MySQL CentOS. Video Backgrounds Free Download Editing Software there. Fedora Install MySQL. Installing MySQL on CentOS. This guide will help you to install MySQL on centos/rhel 7/6/5 and Fedora 25/24/23.
Samba "how to" (smb.conf) Samba Optimization and Speed Tuning; Tools. AES-NI SSL Performance Study; Aria2 tutorial ( metalink bittorrent) Badblocks hard drive. Linux System Administrator with over 8 years experience in administering production level servers (CentOS/Ubuntu/Debian with apache2/nginx, mysql server, etc). In around 15 minutes, the time it takes to install Ubuntu Server Edition, you can have a LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP) server up and ready to go. Upload & Install on Your Server. Set up Piwik quickly on your own machine thanks to the 5-minute installation. See Installation Guide.

Webmin login screen. Webmin screen. That is all!
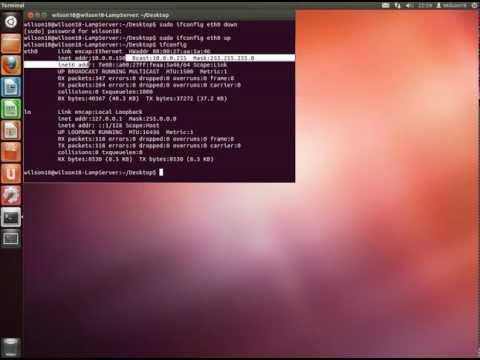
Configuring IPTables in Webmin. HOME . Hopefully you've done so before you installed Debian so they are listed as eth. If you added a second after the install, a reboot will load drivers for it but it won't have an interface name. To add a configuration option you'll need to install Webmin or edit /etc/network/interfaces. I prefer to edit the interfaces file myself. It then shows up in webmin where you can change addresses or other options. INTERFACES: If you plan on using NAT (Network Address Translation, from a single internet IP to multiple private network IP's) to share your internet connection you'll need two hardware network interfaces.
One plugged into your modem or other internet gadget, the other plugged into your local area network, usually through a hub. You probably won't be able to use a router on the internal network so a hub is preferrable.
A router is not really necessary as Debian has a fine DHCP server. I have managed to get a router to act as a hub by using the hub ports alone but it won't work using a crossover cable, from my experience. TIP- If you have a crossover cable (for conecting two comptuers rather than computer to hub) you can use it with a hub by plugging one end it into your internal network adapter and the other end into the . You can then use regular straight through cables to connect the internal net computers to the hub. Bottom Right is the Crossover Cable on Uplink port. Center is my Vista Box and the others are for my XP Scanner system I use to scan pictures. The hub also acts as a repeater so you can also use it to get some extra network reach if cable length is an issue.
MAX length is 1. 00 meters per cable. I get 1. 1 megabytes per second over the 1. Be sure to use the correct power supply for the hub. To get your second NIC working, Install it and reboot. If you've changed hardware (swapped NIC's for newer versions) you can read HERE for a discussion on how to a specific adapter name (eth. MAC address. See the section . Change the eth. X to match your desired adapter name and REBOOT.
You cannot reliably run a webserver and you definitly can't run a mail server without a STATIC INTERNET IP ADDRESS. Ask your ISP to add a DNS A record and an MX record for IP so you can receive mail. Most popular mail systems like Yahoo, Comcast, MSN, Google and others, won't send or accept mail from you unless you have an RLookup. Ask your ISP. Now edit /etc/network/interfaces. Match the entries from that file above and be sure you use the AUTO keywork as below, not HOTPLUG. Basically you need to edit this file then reset the network and watch to make sure both NIC cards come UP correctly.
See below the gray box for how to restart the network. For more information, see interfaces(5).# The loopback network interface, necessary or your network won't work, this is the localhost address. The primary network interface#Broadcast address is always xx. KNOW it to be different#netmask is 2. KNOW different. #Notice the AUTO eth.
The internal Network interface for NAT. You may need to try eth. NIC's. iface eth. Change the address entry below to 1. No need for a gateway, dns or iptables- restore for this adapter unless this is a second internet adapter. To reset your network interfaces, at the console enter: #/etc/init.
If everything went well you'll see the message: Reconfiguring network interfaces.. If you were using Pu. Tt. Y & SSH it will still work if everything came up correctly. Test it by pinging an internet address and an internal net box (cables are pluggin in, right?). If both interfaces respond to pings, YOU'RE SET, continue to WEBMIN below.
If not you'll need to use the console to edit the files above and try again. Just be sure you know which adapter name has which address, one for the internet and the other for your internal network.
WEBMIN: Follow this simple guide and return here when you can login to webmin. ROUTER: If you don't have a hub you may be able to use a hardware router in it's place but it's untested by me and not recommended. It will add an additional address translation layer and duplicates the IPTables NAT function. But, if it's all you have and you need to feed more than one private net computer, you can probably get it to work.
You'll probably need to do this from a desktop computer if your router and internal adapter addresses are the same. Use an address in the same ip range as the server internal adapter. Better yet, use a higher address for the internal adapter and you won't have the problem. At this point you'll have to enter the new router IP in your browser to get it working. Plug in your windoze or linux box(s) and see if they are assigned an address You're on your own with this setup but I can't, offhand, think of a reason it wouldn't work. Email me if it won't and I'll see if I can help, but no guarantees. I got the one above free at a garage sale.
IPTABLES: In Debian Etch the IPTables is already installed or will auto install when you add rules. To restore the rules that were saved enter: #iptables- restore < /etc/webmin/firewall/iptables. First, if you plan on using masquerading you'll need to enable ip forwarding as follows. Failure to do so will cause no end of difficulties getting the masquerading (internet sharing) to work.
This need only be done once for Debian Etch (4. NOTE: In earlier or other versions of Linux the procedure was to use . However this is no longer the correct method in Debian Etch and later versions.
Use the procedure below and there is no need to write a script. The setting is carried on reboot. Activate IP forwarding in /etc/sysctl. These are my rules, the first DROP is for a system that recently attempted to hack my SSH & FTP ports. You will probably not see any rules at all.
At the bottom of the page is a button marked . Near the bottom is an option marked.
Block all except SSH, IDENT, ping and high ports on interface: Select this option and your internet adapter. Mine is eth. 2, but most are eth.
See. You want to select the adapter that connects to the internet (it will have your STATIC internet IP). In the example above I have the following ports open: 2. I have running. If you want to change the default, select the . Press SAVE and then press APPLY CONFIGURATION. Test your open ports if you have a local tool to do so. If not you'll need to enable NAT first so you can use a private net computer on your internal network to find a site on the internet.
NAT: Now, to enable NAT on an internal network you'll need a separate interface, of course. Mine is eth. 1 and my internal network gateway address is: 1. You'll need to know this address, even if you run DHCP.
The IP address of the internal gateway (IP of the second NIC) is arbitrary but use 1. I changed mine to allow static IP addresses below it and to prevent conflic if I had to use my router again. If you haven't already discovered, more than one gadget cannot have the same IP address so If I use 1. IP I can't even get to my Router if I need to fiddle with it.
If you aren't sure, use 1. Network Configuration screen for the adapter you are using, then SAVE and APPLY . You should be able to ping it from a private net computer (ping 1. NAT is not working, and Webmin should also work in a browser from an internal network computer as long as you connect to http: //1. Be sure to use 2.
This will allow you to use Webmin even if your NAT is not working for internet access. To enable NAT redirection on the internal adapter look at the top of the screen for the drop down box that says . You'll see no rules listed. We need to add only one rule to enable NAT. Under the POSTROUTING heading (bottom of the screen) press the ADD RULE button on the far right. At the top tick the box that says .
Now down on the lower portion of the screen find the box marked . Mine is eth. 2 so I select . Hit SAVE at the bottom of the screen to save this rule then select APPLY CONFIGURATION. Mine looks like this: You should now be able to browse the internet on your NAT address boxes through your internal network interface.