Difference Between Trickling Filter And Activated Sludge Process
Activated Sludge Process. Sludge digestion is carried out in the absence of free oxygen by anaerobic organisms.
Search metadata Search full text of books Search TV captions Search archived web sites Advanced Search. Get information, facts, and pictures about water pollution at Encyclopedia.com. Make research projects and school reports about water pollution easy with credible.
It is, therefore, anaerobic decomposition. The solid matter in raw sludge is about 7.
Much of the water in wastewater sludge is . The facultative and anaerobic organisms break down the complex molecular structure of these solids setting free the . For purposes of simplification, the anaerobic degradation of domestic sludges occurs in two steps.
The environmental impact of paper is significant, which has led to changes in industry and behaviour at both business and personal levels. Driver Intel Ich8m Sata Ahci Controller Driver more. With the use of modern. What is Civil Engineering? What is Civil Engineering Technology? Civil Engineering is said to be the biggest and most.
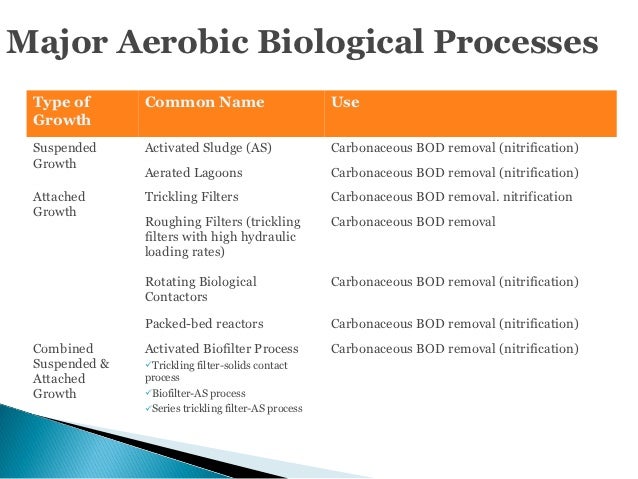
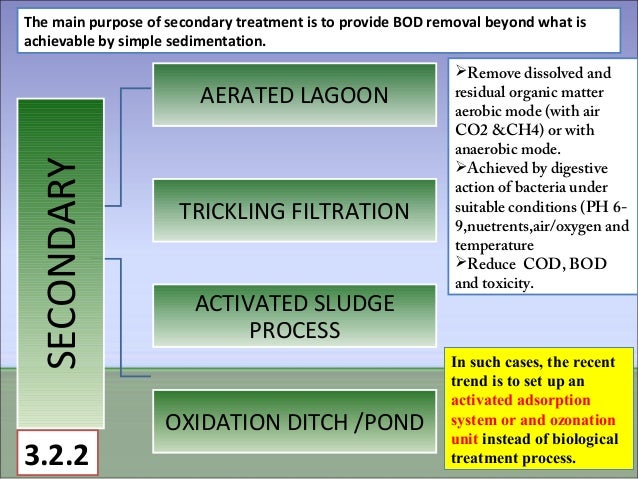
Some of the major important types of wastewater treatment process are as follows: 1. Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) 2. Sewage Treatment Plants (STP) 3. Common and. Some of the major process of secondary or biological treatment are as follows: (i) Activated Sludge Process (ii) Trickling Filters. The biological process of sewage. Coagulation and Flocculation in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Coagulation and flocculation are an essential part of drinking water treatment as well as wastewater. Examples of filtration include. The coffee filter to keep the coffee separate from the grounds. HEPA filters in air conditioning to remove particles from air.
In the first step, acid forming bacteria attack the soluble or dissolved solids, such as the sugars. From these reactions. Mapa Polski Gps Tomtom Download Map. This is known as the stage of acid fermentation and proceeds rapidly. It is followed by a period of acid digestion in which the organic acids and nitrogenous compounds are attacked and liquefied at a much slower rate. In the second stage of digestion, known as the period of intensive digestion, stabilization and gasification, the more resistant nitrogenous materials, such as the proteins, amino- acids and others, are attacked.
The p. H value must be maintained from 6. Large volumes of gases with a 6. Methane is an odorless, highly inflammable gas which can be used as a fuel. The organisms which convert organic acids to methane and carbon dioxide gases are called methane formers. The solids remaining are relatively stable or only slowly putrescible, can be disposed of without creating objectionable conditions and have value in agriculture.
Cetylpyridinium chloride
FOREWORD In 1947, a "Committee on Development of Uniform Standards for Sewage Works" was created by the group now known as the Great Lakes.
The whole process of sludge digestion may be likened to a factory production line where one group of workers takes the raw material and conditions it for a second group with different . Fresh. wastewater solids are being added at frequent intervals with the stabilized solids being removed for further treatment or disposal at less frequent intervals. The supernatant digester liquor, the product of liquefaction and mechanical separation is removed frequently to make room for the added fresh solids and the gas is, of course, being removed continuously. While all stages of digestion may be proceeding in a tank at the same time with the acids produced in the first stage being neutralized by the ammonia produced in subsequent stages, best and quickest results are obtained when the over- all p. H of 6. 8 to 7. 4 predominates.
The first stage of acid formation should be evident only in starting up digestion units. Once good alkaline digestion is established, the acid stage is not apparent unless the normal digestion becomes upset by overloading, poisonous chemicals or for other reasons. It is critical to the overall process to maintain balanced populations of acid formers and methane formers.
The methane formers are more sensitive to environmental conditions and slower growing than.